- Ansible
- 部署
- Ansible命令选项
- Ansible主机清单(inventory)
- Ansible模块
- Ansible剧本
- 剧本与变量
- 剧本流程控制(tasks控制)
- Roles
- 部署LNMP环境
- Ansible jinja2模版
- Ansible优化
- 参考教程
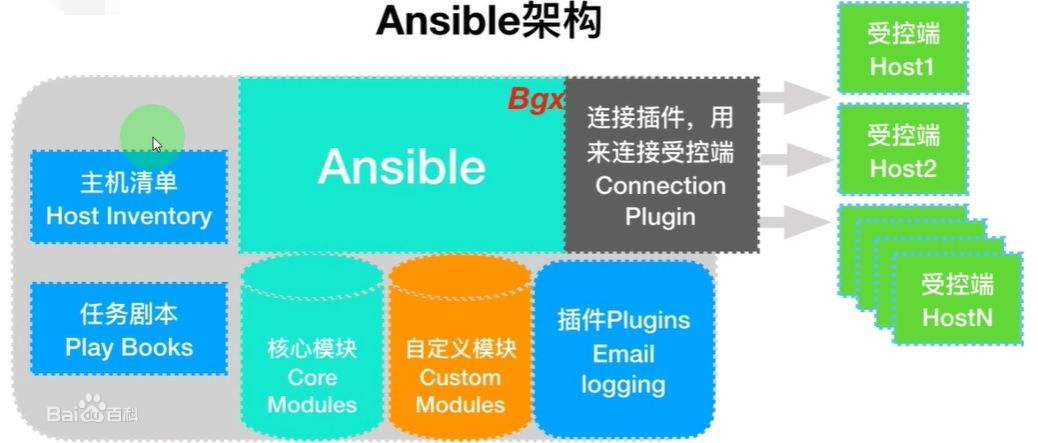
Ansible
简介
ansible是一个同时管理多个远程主机的软件,必须是任意可以通过ssh登录的机器,因此ansible可以管理的机器有
- 远程虚拟机
- 物理机
- 也可以直接管理本机机器
ansible通过ssh协议实现了管理节点(安装了ansible服务的机器),被管理节点(被管理的机器节点)的通信,只能是通过ssh协议登录的主机,就可以完成ansible自动化部署操作
- 批量文件分发
- 批量数据复制
- 批量数据修改,删除
- 批量自动化安装软件服务
- 批量服务启停
- 校本化,自动批量服务部署
特点
ansible的编排引擎可以出色的完成各种任务配置管理,ansible在流程控制,资源部署等方便很强大,并且ansible无须安装客户端软件,管理简介,使用yaml配置文件语法,功能强大,便于维护。ansible基于python语言开发,主要由python的两个ssh处理模块,paramiko,以及PyYAML模块
- 安装部署简单
- 管理主机便捷,支持多台主机并行管理
- 无须安装被管理节点的客户端(no agent),且无须占用客户端的其他端口,仅仅使用ssh服务即可
- 不仅仅支持python,还支持其他语言的二次开发
- 不用root用户也可执行,降低系统权限
部署
环境
- 一台管理机器(安装了ansible的服务端)
- 两台被管理机器(配置好ssh服务,以及关闭防火墙)
安装
# 管理节点执行
yum install epel-release ansible libselinux-python -y
# 检查ansible软件安装情况,查询配置文件,和可执行命令
rpm -ql ansible | grep -E '/etc|^/usr/bin'
# 检查版本
ansible --version
# 工作节点执行
yum install epel-release libselinux-python -y
Ansible命令选项
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| -i | inventory list 指定主机清单 |
| -m | module 指定模块 |
| -a | action 指定动作(一般是模块中选项,命令) |
| -k | 询问密码验证 |
| -u | 指定运行的用户 |
Ansible主机清单(inventory)
主机进行分组
# 创建指定目录
mkdir -p /server/scripts/ansible
# 备份现有的主机清单
cp /etc/ansible/hosts{,.ori}
# 写入主机清单到文件
tee /server/scripts/ansible/hosts <<-'EOF'
[web]
192.168.50.133
[db]
192.168.50.133
[nfs]
192.168.50.133
EOF
# 执行命令,all代表全部主机清单
ansible -i hosts all|web -m ping
划分子组
对多个/单个已经划分好的组,进行再次分组
hosts
[web]
192.168.50.133
[db]
192.168.50.133
[nfs]
192.168.50.133
# 给[db]、[nfs]合并叫data组,data组下有两个子组
[data:children]
db
nfs
主机清单与密码
用户名和密码写在主机清单
# 手动在主机清单中指定用户名和密码
[web]
192.168.50.133 ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=root
# 根据组进行用户名和密码的设置,all表示所有
[web:vars]
ansible_ssh_port=22
ansible_user=root
ansible_ssh_pass=root
- ansible_host:主机地址
- ansible_ssh_port:端口,默认是22端口
- ansible_user:认证的用户
- ansible_ssh_pass:用户认证的密码
验证命令
ansible server -a 'hostname'
ssh密码认证方式管理机器
ansible是直接利用linux本地的ssh服务,以及一些远程的ssh操作,一般情况下客户端的ssh服务默认都是开启的,无须额外管理
# 手动ssh连接主机
ssh root@192.168.50.133
# 管理节点执行,告诉其他被管理的机器,需要执行什么命令,以及用什么用户去执行
ansible server -m command -a 'hostname' -k -u root
192.168.50.133 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
node01
- -m:指定功能模块,默认就是command模块
- -a:告诉模块需要执行的参数
- -k:询问密码验证
- -u:指定运行的用户
配置免密登录
每次执行ansible命令的时候,都需要输入ssh的认证密码,也就是root的密码,如果不同的主机密码不一致,还得输入多次才行,因此可以配置如下的登录方式
ssh密钥方式批量管理主机
比起hosts文件的密码参数更安全
# 创建ssh密钥对
ssh-keygen -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa -P "" > /dev/null 2>&1
# 检查公私钥文件
ls ~/.ssh/
- -f:指定生成的文件路径
- -P:省略输入密码
> /dev/null 2>&1:标准输出和标准错误重定向到黑洞中
批量分发ssh密钥脚本
#!/bin/bash
# 清空密钥对
rm -rf ~/.ssh/id_rsa*
# 生成新的密钥对
ssh-keygen -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa -P "" > /dev/null 2>&1
# 密码
SSH_PASS=root
# 公钥路径
KEY_PATH=~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
for ip in 132 133
do
sshpass -p$SSH_PASS ssh-copy-id -i $KEY_PATH "-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no" 192.168.50.$ip
done
# 非交互式分发公钥命令需要用sshpass指定SSH密码,通过-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no 跳过SSH连接确认信息
此时在管理机器上再次连接客户端机器,就无须输入账号密码了,可以尝试使用ansible命令进行连接
ansible server -m command -a 'uname -a'
此时已经无须输入密码,即可远程管理
Ansible模块
- Ansible AD-Hoc ansible命令行批量执行命令(使用各种模块)
- 官方文档:https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections/ansible/builtin/index.html#plugins-in-ansible-builtin
| ansible模块 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| ping | 检查ansible与主机连通性 |
| 命令/脚本模块 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| command | 批量执行简单命令(不含特殊符号)默认的模块 |
| shell | 批量执行shell命令 |
| scripts | 分发脚本并执行,把管理机器上的脚本远程的传输到被管理节点上去执行 |
命令脚本相关模块
支持的参数和解释
- chdir 在执行命令之前,通过cd进入该参数指定的目录,例:
ansible server -m command -a "pwd chdir=/tmp/" - creates 定义一个文件是否存在,如果存在则不执行该命令,如果存在该文件,则执行命令,例:
ansible 192.168.50.133 -m command -a "pwd creates=/server" - free_form 参数信息中可以输入任何的系统指令,实现远程管理
- removes 定义一个文件是否存在,如果存在该文件,则执行命令,如果不存在,则跳过,例:
ansible 192.168.50.133 -m command -a "ls /opt removes=/opt"
shell
# 使用格式
# ansible 指定主机清单 主机组 指定模块 指定动作(参数)
ansible -i hosts lb -m shell -a 'hostname'
command
ansible默认的模块(不指定模块,默认就使用command模块),command适用于执行简单的命令(不支持特殊符号)
ansible -i hosts lb -a 'hostname'
scripts
scripts模块分发脚本并执行
# yum.sh
#!/bin/bash
yum install -y ipvsadm
# 执行脚本
ansible -i hosts lb -m script -a 'yum.sh'
文件相关模块
file
文件/目录创建,删除
| 参数 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| path | 路径(目录,文件)必需 |
| src | 源文件一般用于link(创建软链接模式)用于指定源文件 |
| state | 状态(模式)state=directory创建目录 state=file(默认)更新文件,如果文件不存在也不创建 state=link创建软链接 state=touch创建文件 |
创建目录
ansible -i hosts all -m file -a 'path=/server/scripts/python state=directory'
创建文件
ansible -i hosts all -m file -a 'path=/server/scripts/python/lidao.py state=touch'
创建软链接
ansible -i hosts all -m file -a 'src=/server/scripts/python path=/python state=link'
# 检查
ansible -i hosts all -a 'ls -ld /python'
copy
远程复制(ansible管理机器上文件复制到对应的节点)
| 参数 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| src | source源文件路径 |
| dest | destination目标路径 |
| backup | backup=yes,则会在覆盖前进行备份 |
| mode | 修改权限 |
| owner | 修改为指定所有者 |
| group | 修改为指定用户组 |
# 分发文件到所有机器
ansible -i hosts all -m copy -a 'src=/etc/hostname dest=/tmp/'
# 分发目录到所有机器(不推荐)
ansible -i hosts all -m copy -a 'src=/etc/sysconfig dest=/tmp/'
# 注意:ansible中对于路径加/区别
# 不加/ 目录+目录内容
# 加/ 目录的内容
# 传输过程中修改权限
ansible -i hosts web -m copy -a 'src=/etc/hostname dest=/opt/ mode=644 owner=nginx group=nginx'
# 批量分发hosts文件,如果文件存在则备份
ansible -i hosts all -m copy -a 'src=/etc/hosts dest=/etc/hosts backup=yes'
服务管理
- 开机自启动/不自启动
- 服务开启,关闭/重启
systemd
类似于systemctl,CentOS7、CentOS8都可以用
| 参数 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| name | 用于指定服务名称 |
| enabled | yes开机自启动 |
| state | 表示服务开,关,重启 state=started开启 state=stopped关闭 state=reloaded重读配置文件(需要服务支持,如nginx) state=restarted重启(关闭再开启) |
| daemon-reload | yes是否重新加载对应的服务的管理配置文件 |
# 服务的开机自启动
ansible -i hosts lb -m systemd -a 'name=crond enabled=yes'
# 服务的开启关闭重启等操作
ansible -i hosts lb -m systemd -a 'name=crond enabled=yes state=restarted'
service
一般应用于CentOS5、CentOS6。CentOS7、CentOS8也可以用
| 参数 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| enabled | 开机自启动 |
| name | 服务名称 |
| state | 服务开关重启 |
| runlevel | 运行级别 |
软件包管理
- 配置yum源:yum_repository
- 通过yum安装软件:yum
yum_repository
| 参数 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| name | yum源中名字[epel] |
| description | yum源的注视说明 对应的是name的内容 |
| baseurl | yum源中baseurl下载地址 |
| enabled | 是否启动这个源 yes/no |
| gpgcheck | 是否启动gpgcheck功能 yes/no |
| file | 指定yum源的文件 自动添加.repo 默认与模块名字一致 |
/etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo
[epel] # 模块名字
name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - $basearch # 注释
#baseurl=http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/$basearch # 下载地址
metalink=https://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/metalink?repo=epel-7&arch=$basearch
failovermethod=priority
enabled=1 # 是否开启这个源
gpgcheck=1 # 是否开启gpgcheck功能
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-7 # 如果开启gpgcheck指定的路径和文件
添加nginx yum源
官方地址:https://nginx.org/en/linux_packages.html#RHEL
# 批量添加nginx yum源
[nginx-stable]
name=nginx stable repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=true
ansible -i hosts lb -m yum_repository -a 'name="nginx-stable" description="nginx stable repo" baseurl="http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/" enabled=yes gpgcheck=no file=nginx'
# 检查文件
ansible -i hosts lb -a 'cat /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo'
yum
| 参数 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| name | 指定软件包名字 |
| state | installed安装(present) removed删除(absent) latest安装或更新 |
# 安装nginx
ansible -i hosts lb -m yum -a 'name=nginx state=present'
# 升级
ansible -i hosts lb -m yum -a 'name=nginx state=latest'
下载软件包
get_url
下载软件包到本地
| 参数 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| url | 指定要下载的地址 |
| dest | 下载的目标路径 |
# 先创建目录
ansible -i hosts all -m file -a 'path=/server/tools/ state=directory'
# 下载软件包到所有机器的/server/tools/目录下
ansible -i hosts all -m get_url -a 'url="https://mirrors.aliyun.com/zabbix/zabbix/4.0/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-agent-4.0.0-2.el7.x86_64.rpm?spm=a2c6h.25603864.0.0.63307b84NthAYJ" dest=/server/tools/'
# 检查下载的软件包
ansible -i hosts all -a 'ls -l /server/tools/'
# 安装rpm包
ansible -i hosts all -m yum -a 'name=/server/tools/zabbix-agent-4.0.0-2.el7.x86_64.rpm state=present'
# 查看安装的软件包
ansible -i hosts all -m shell -a 'rpm -qa | grep zabbix'
# 启动服务与检查状态
ansible -i hosts all -m systemd -a 'name=zabbix-agent enabled=yes state=started'
ansible -i hosts all -m shell -a 'ps -ef|grep zabbix'
系统管理
mount
远程挂载模块
| 参数 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| fstype | 指定文件系统 |
| src | 源地址(nfs地址172.16.1.31/data) |
| path | 挂在点(要把源挂载到哪里) |
| state | absent卸载并修改fstab unmounted卸载不修改/etc/fstab present仅修改/etc/fstab不挂载 mounted挂载并修改/etc/fstab remounted重新挂载 |
# 让web挂载nfs共享存储 挂载到/mnt下
ansible -i hosts web -m mount -a 'fstype=nfs src=172.16.1.31:/wwwdata path=/mnt state=mounted'
# 卸载
ansible -i hosts web -m mount -a 'fstype=nfs src=172.16.1.31:/wwwdata path=/mnt/ state=absent'
# 检查
ansible -i hosts web -a 'df -h'
ansible -i hosts web -a 'grep wwwdata /etc/fstab'
cron
定时任务模块
| 参数 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| name | 定时任务名字,对应注释内容 |
| minute | 分钟 minute=”*/2” |
| hour | 小时 |
| day | 日期 |
| month | 月份 |
| week | 周几 |
| job | 指定命令或脚本(定向到空)job=”/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com &>/dev/null” |
| state | present添加定时任务 absent删除 |
| disabled | 注释定时任务(会在cron脚本前添加注释#)yes/no |
# 批量给所有机器添加时间同步功能
# sync time
*/2 * * * * /sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com &>/dev/null
# 检查软件是否安装 批量安装ntpdate
ansible -i hosts all -m yum -a 'name=ntpdate state=present'
# 批量添加定时任务,自动同步时间
ansible -i hosts all -m cron -a 'name="sync time" minute="*/2" job="/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com &>/dev/null" state=present'
# 检查
ansible -i hosts all -a 'crontab -l'
# 删除定时任务
ansible -i hosts all -m cron -a 'name="sync time" state=absent'
# 注释定时任务
ansible -i hosts all -m cron -a 'name="sync time" minute="*/2" job="/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com &>/dev/null" state=present disabled=yes'
用户管理
group
| 参数 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| name | 指定用户组名字 |
| gid | 指定组的gid |
| state | present添加 absent删除 |
# 添加用户组wwww gid1999
groupadd -g 1999 wwww
ansible -i hosts web -m group -a 'name=wwww gid=1999 state=present'
user
| 参数 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| name | 指定用户名 |
| uid | 指定uid |
| group | 指定用户组 |
| shell | 指定命令解释器 |
| create_home | 是否创建家目录 |
| state | present添加 absent删除 |
# 添加用户wwww 指定uid1999 指定用户组是wwww 不创建家目录
useradd -u 1999 -g wwww -s /sbin/nologin -M wwww
ansible -i hosts web -m user -a 'name=wwww uid=1999 group=wwww shell=/sbin/nologin create_home=no state=present'
# 检查
ansible -i hosts web -a 'id wwww'
模块总结
| 模块分类 | |
|---|---|
| 命令和脚本模块 | command模块,默认的模块,执行简单命令,不支持特殊符号 |
| shell模块,执行命令,支持特殊符号 | |
| script模块,分发脚本并执行 | |
| 文件 | file创建目录,文件,软链接 |
| copy远程分发文件,修改权限,所有者,备份 | |
| 服务 | systemd服务管理 |
| service服务管理 | |
| 软件包 | yum源yum_repository |
| yum命令 | |
| get_url下载软件 | |
| 系统管理 | mount模块挂载 |
| cron模块定时任务 | |
| 用户管理 | group模块 管理用户组 |
| user模块 管理用户 | |
| 其他 | 压缩解压,rsync模块,数据库模块 |
| 调试模块 | ping模块检查ansible与其他节点连通性ansible -i hosts all -m ping |
| debug模块用于检查/显示变量 |
模块帮助查询
ansible-doc命令
# 列出所以的ansible支持的模块
ansible-doc -l
# 查看某个模块的具体用法参数
ansible-doc -s command
Ansible剧本
- Ad-hoc命令使用ansible模块,单次执行方便,对于重复执行(部署环境nginx源,php源)
- 对于重复性操作与部署推荐使用剧本(脚本),剧本的本质,使用模块+固定格式(对齐)
- 官方文档:https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/playbook_guide/index.html
剧本格式
-
yaml格式/语言
.yaml,.yml结尾 -
具体书写注意事项
- 同一个层级的内容对齐
- 不同层级的通过2个空格对齐
playbook组成
#playbook
---
#play:一般用于指定不同的主机
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
vars:
file_name:
#task:指定了机器后,让这些机器执行的模块
tasks:
- name: touch new files
shell: touch /tmp/\{\{file_name\}\}
批量创建文件
vim touch.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: touch file
shell: touch /tmp/file
执行剧本
# --check/-C:检查剧本格式
ansible-playbook -i hosts touch.yml -C
# 执行剧本
ansible-playbook -i hosts touch.yml
附:执行剧本时控制台图案输出工具
yum install -y cowsay
# 对应配置文件
vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
批量创建cron定时任务
vim cron.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: add time sync
cron: name="sync time" minute="*/2" job="/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com &>/dev/null" state=present
执行剧本
ansible-playbook -i hosts cron.yml
# 检查
ansible -i hosts all -a 'crontab -l'
批量添加用户和组
vim useradd.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: groupadd
group: name=wwww gid=1999 state=present
- name: useradd
user: name=wwww uid=1999 group=wwww shell=/sbin/nologin create_home=no state=present
执行剧本
ansible-playbook -i hosts useradd.yml
# 检查
ansible -i hosts web -a 'grep wwww /etc/passwd /etc/group'
ansible -i hosts web -a 'id wwww'
批量下载软件包到指定目录安装并启动
vim install.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: mkdir
file: path=/server/tools/ state=directory
- name: download rpm
get_url: url="https://mirrors.aliyun.com/zabbix/zabbix/4.0/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-agent-4.0.0-2.el7.x86_64.rpm?spm=a2c6h.25603864.0.0.63307b84NthAYJ" dest=/server/tools/
- name: install rpm
yum: name=/server/tools/zabbix-agent-4.0.0-2.el7.x86_64.rpm state=present
- name: systemctl start && enable
systemd: name=zabbix-agent enabled=yes state=started
执行剧本
ansible-playbook -i hosts install.yml -C
ansible-playbook -i hosts install.yml
Ansible playbook与Ad-Hoc的关系
- playbook是对Ad-Hoc的一种编排方式
- playbook可以持久运行(重复),而Ad-Hoc只能临时运行
- playbook适合复杂的任务,而Ad-Hoc适合做快速简单的任务(检查,查询,巡检)
- playbook能控制任务执行的先后顺序
- ad-hoc用于检查,测试,临时获取数据
- playbook剧本适用于,重复性操作(部署环境,服务,初始化操作)
剧本与变量
定义与使用变量
- 命令行定义
- 在剧本中,专门文件中定义变量
-
ansible内置变量(facts)
- 通过剧本play部分中vars定义变量,剧本中play部分vars_files指定变量文件,通过group_vars指定主机组共享变量文件
- 实现echo $?. 返回值/返回信息,命令执行结果/显示. register模块下面加上register把模块输出存放在一个变量中,通过debug msg输出变量内容,变量.rc 变量.stdout 变量.stderr
- facts变量,比较容易的快速去除被管理端:ip,主机名,发行版本,系统版本,内存,网卡,磁盘
命令行定义变量
test-playbook.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: print var
debug:
msg: '变量file的内容是 \{\{ file \}\}'
执行命令
ansible-playbook -i hosts test-playbook.yml -e "file=/etc/hostname"
主机清单定义变量
hosts
[web]
192.168.50.133
[db]
192.168.50.133
[nfs]
192.168.50.133
[data:children]
db
nfs
[web:vars]
port=80
[db:vars]
port=3306
test-web-vars-playbook.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: print var
debug:
msg: 变量port的内容是 \{\{ port \}\}
剧本中与专门文件定义变量
剧本中
# 定义变量file,变量内容/etc/hostname
debug
# file=/etc/hostname
# echo $file
vars-playbook.yml
- hosts: web
vars:
file: /etc/hostname
tasks:
- name: print var
debug:
msg: 变量file的内容是 \{\{ file \}\}
测试运行
ansible-playbook -i hosts -C vars-playbook.yml
ansible-playbook -i hosts vars-playbook.yml
注意:变量在开头时要加上双引号或单引号,如msg: "\{\{ file \}\}变量file"
变量文件
vars-file.yml
file: /etc/hostname
dir: /root
vars-playbook.yml
- hosts: web
vars_files: ./vars-file.yml
tasks:
- name: print var
debug:
msg: '\{\{ dir \}\}变量file的内容是 \{\{ file \}\}'
根据主机清单分组自动识别变量
通过主机清单里面的分组进行变量共享,比如:eg web服务器 port 80 data服务器 port 873
group_vars/
lb/vars.yml #存放lb组的变量
web/vars.yml #存放web组的变量
data/vars.yml #存放data组的变量
all/vars.yml # 所有主机共用的变量
创建目录
mkdir -p /server/scripts/ansible/group_vars && cd /server/scripts/ansible/group_vars
mkdir {lb,web,data,all}
创建文件
data/vars.yml
port: 873
web/vars.yml
port: 80
group-vars.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: print var
debug:
msg: '当前服务的端口号是\{\{ port \}\}'
- hosts: data
tasks:
- name: print var
debug:
msg: '当前服务的端口号是\{\{ port \}\}'
执行命令
ansible-playbook -i hosts -C group-vars.yml
变量定义小结
| 定义方式 | |
|---|---|
| 命令行 | 临时定义创建 |
| 主机清单 | |
| 剧本中定义变量 | 常用,vars: 好处:方便,易于理解,缺点:仅当前剧本生效,其他剧本还需要重新定义 |
| 变量文件 | 变量都放在一个文件中,vars_files方便管理与维护,无法针对某些主机(分组)进行定义 |
| 根据分组(主机清单)定义变量 | group_vars/{lb,web,data}/vars.yml存放变量 group_vars/all/vars.yml 定义后剧本中自动根据组识别 |
Ansible内置变量(facts变量)
facts变量是在运行剧本的时候ansible收集的每台机器的信息
# 查看ansible facts变量内容
ansible -i hosts web -m setup
facts-var.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: print facts vars
debug:
msg: "facts 变量 \{\{ ansible_default_ipv4.address \}\}"
执行命令
ansible-playbook -i hosts facts-var.yml
register类型变量
Ansible模块运行时,会返回一些结果,可以把这些返回值存储到变量之中,通过调用对应的变量名,获取这些结果,这种将模块的返回值写入到变量的方法叫做变量注册
获取日期,创建以日期命令的文件
time=`date +%F_%w` # 执行命令/模块,然后把命令/模块的结果保存
register-vars.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: get date
command: date +%F_%w
register: time
- name: touch file
file:
path: '/tmp/\{\{ time.stdout \}\}.txt'
state: touch
执行命令
ansible-playbook -i hosts register-vars.yml
ansible变量与应用场景
| 变量定义方式 | |
|---|---|
| 用户自己定义 | 常用剧本中通过vars定义变量,通过group_vars定义变量(根据主机清单分组)其他方式:vars_files主机清单文件 |
| ansible内置(facts变量) | 用于获取系统基本信息,会导致剧本执行速度减慢,可以在hosts部分通过gather_facts: false关闭 |
| register变量 | 注册变量(临时变量) |
剧本流程控制(tasks控制)
- handler
- when
- loop(with_items)循环
handler
分发nginx配置文件,通过notify监控某个模块,发生变化后,触发对应handlers
handler-playbook.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: fenfa nginx conf
copy:
src: ansible.nginx.conf
dest: /etc/nginx/conf.d/
backup: yes
notify:
- nginx restart
handlers:
- name: nginx restart
systemd:
name: nginx
state: reloaded
执行命令
ansible-playbook -i hosts handler-playbook.yml
when条件
when一般配置模块实现只有指定条件下才运行对应的模块
when: ( ansible_distribution == "Ubuntu" ) # 如果系统的发行版本是Ubuntu则运行模块
when: ( ansible_hostname is match("web"|"lb") ) # 主机名包含web或lb 配置nginx源
when: ( ansible_hostname is not match("web"|"lb") )
给web服务器和lb服务器配置nginx yum源
when-add-nginx-yum.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: add nginx yum repo
yum_repository:
name: "nginx-stable"
description: "nginx yum repo"
baseurl: "http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/"
enabled: yes
gpgcheck: no
file: nginx
when: ( ansible_hostname is match("web"|"lb") )
- when一般与ansible facts变量一起使用,判断主机/判断系统类型
- when也可以与register变量一起搭配
循环
当需要批量重启或停止服务时,可以通过with_items实现
with-item-restart-service.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: restart
systemd:
name: "\{\{ item \}\}"
state: stopped
with_items:
- nginx
- crond
- php-fpm
执行命令
ansible-playbook -i hosts with-item-restart-service.yml
批量添加用户,指定用户名和uid
with-item-add-user.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: add user
user:
name: "\{\{ item.name \}\}"
uid: "\{\{ item.uid \}\}"
with_items:
- { name: 'lidao997', uid: '997' }
- { name: 'lidao8848', uid: '8848' }
执行命令
ansible-playbook -i hosts with-item-add-user.yml
- 循环小结
- 配合一些模块实现批量操作,比如:批量重启/关闭/开启服务,批量添加用户
- with_items(常用)loop(功能多)
调试使用:tag标签
tag标签:给模块设置1个标签(或多个)执行剧本的时候可以指定运行标签
--skip-tags #跳过指定的标签
-t --tags #运行指定的标签
--list-tags #列出当前剧本的标签
tags-install-zbx-agent.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: mkdir
file: path=/server/tools/ state=directory
tags:
- mkdir
- install
- name: download rpm
get_url: url="https://mirrors.aliyun.com/zabbix/zabbix/4.0/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-agent-4.0.0-2.el7.x86_64.rpm?spm=a2c6h.25603864.0.0.63307b84NthAYJ" dest=/server/tools/
tags:
- download
- install
- name: install rpm
yum: name=/server/tools/zabbix-agent-4.0.0-2.el7.x86_64.rpm state=present
tags:
- install_agent
- install
- name: systemctl start && enable
systemd: name=zabbix-agent enabled=yes state=started
tags:
- start_srv
执行命令
ansible-playbook -i hosts --tags mkdir,download tags-install-zbx-agent.yml
调试使用:忽略错误
- ignore_errors 忽略错误,调试的时候即使报错也要继续运行(一般用于调试与检查语法的时候)
register-ignore-errors.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: get date
command: date +%F_%w
register: time
- name: touch file
file:
path: '/tmp/\{\{ time.stdout \}\}.txt'
state: touch
ignore_errors: yes
- name: mkdir /tmp/lidao.txt
file:
path: /tmp/lidao.txt
state: directory
执行命令
ansible-playbook -i hosts -C register-ignore-errors.yml
ansible include功能
主剧本,拆出来子剧本
#拆分,主剧本中记录步骤
- hosts: all
tasks:
- include_tasks: 01-yum.yml
- include_tasks: 02-install.yml
- include_tasks: 03-config.yml
- include_tasks: 04-db.yml
- include_tasks: 05-code.yml
#环境与yum源
- name: 配置基础环境
yum_repository: 配置nginx yum源
- name: 配置基础环境
yum_repository: 配置php源
#服务部署
- name: 安装服务,nginx,php,mariadb
yum: name=nginx,php,maraidb
#服务配置
- name: 配置nginx
template: 分发站点配置文件和主配置文件
- name: 配置php
template: 分发php
#数据库配置
- name: 数据库操作
mysql_db和mysql_user
#代码
- name: 代码(分发,解压,权限,所有者)
Roles
- 一个对于ansible剧本的目录的规划,目标是让剧本中内容分门别类的放在不同的目录中
主剧本结构
- hosts: all
roles:
- role: basic
- hosts: web
roles:
- role: nginx
- role: php-fpm
basic/ #主剧本中指定的名称,名字代表功能
basic/files/ #存放不含变量的配置(压缩包)
basic/handlers/main.yml #handlers部分,执行的handlers
basic/tasks/main.yml #剧本中tasks部分
basic/templates/xx.j2 #使用变量模版文件
创建目录
mkdir -p nginx/{files,templates,tasks,handlers}
创建文件
use-roles-nginx.yml
- hosts: web
gather_facts: false
roles:
- role: nginx
nginx/tasks/main.yml
- name: fenfa nginx conf
template:
src: ansible.nginx.conf.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/conf.d/ansible.nginx.conf
backup: yes
notify:
- nginx restart
nginx/handlers/main.yml
- name: nginx restart
systemd:
name: nginx
state: reloaded
nginx/templates/ansible.nginx.conf.j2
cp ansible.nginx.conf nginx/templates/ansible.nginx.conf.j2
执行命令
ansible-playbook -i hosts use-role-nginx.yml
部署LNMP环境
主机清单
创建目录
mkdir -p /server/scripts/project && cd /server/scripts/project
inventory
[lb]
192.168.50.133
[web]
192.168.50.133
[db]
192.168.50.133
[nfs]
192.168.50.133
# 给[db]、[nfs]合并叫data组,data组下有两个子组
[data:children]
db
nfs
roles内容
创建目录
mkdir -p {basic,nginx-web,php,nfs,db}/{files,templates,tasks,handlers} group_vars/all/
basic
basic/tasks/main.yml
#优化ssh
- name: ssh config
block:
#备份sshd配置文件
- name: backup sshd config
copy:
src: /etc/ssh/sshd_config
dest: /etc/ssh/sshd_config.bak
notify: Restart SSH
#修改sshd配置文件
- name: modify sshd config
lineinfile:
path: /etc/ssh/sshd_config
regexp: '^#?PermitRootLogin'
line: 'PermitRootLogin no'
#禁用空密码登录
- name: disabled blank pass
lineinfile:
path: /etc/ssh/sshd_config
regexp: '^#?PermitEmptyPasswords'
line: 'PermitEmptyPasswords no'
#禁用SSH密码登录
- name: disabled ssh pass
lineinfile:
path: /etc/ssh/sshd_config
regexp: '^#?PasswordAuthentication'
line: 'PasswordAuthentication no'
#关闭防火墙
- name: close firewalld
block:
#停止firewalld服务
- name: stop firewall service
service:
name: firewalld
state: stopped
#禁止firewalld服务开机启动
- name: disabled firewalld
service:
name: firewalld
enabled: no
#配置yum源base,epel源
- name: config yum and epel repo
block:
#安装epel-release软件包
- name: install epel-release package
yum:
name: epel-release
state: present
#备份yum源配置文件
- name: backup yum config
copy:
src: /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo
dest: /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.bak
#下载base源配置文件
- name: download yum repo
get_url:
url: http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
dest: /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo
mode: '0644'
validate_certs: no
#刷新yum缓存
- name: flush yum cache
command: yum clean all
basic/handlers/main.yml
#重启SSH服务
- name: Restart SSH
service:
name: sshd
state: restarted
nginx
nginx/tasks/main.yml
#配置yum源
- name: add nginx yum repo
yum_repository:
name: "nginx-stable"
description: "nginx yum repo"
baseurl: "http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/"
enabled: yes
gpgcheck: no
file: nginx
tags:
- add_nginx_repo
#安装nginx
- name: install nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: present
tags:
- install_nginx
#配置文件
- name: config nginx.conf
template:
src: nginx.conf.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
backup: yes
tags:
- config_nginx
#启动nginx
- name: start nginx
systemd:
name: nginx
enabled: yes
state: restarted
tags:
- start_nginx
nginx/templates/nginx.conf.j2
user \{\{ web_user \}\};
worker_processes auto;
pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}
group_vars/all/main.yml
web_user: nginx
php
php/tasks/main.yml
#配置php源
- name: config php repo
template:
src: php.repo.j2
dest: /etc/yum.repos.d/php.repo
backup: yes
#安装PHP
- name: install php dependents
yum:
name:
- php-fpm
- php
- php-common
- php-cli
state: present
#发送配置文件
- name: fenfa www.conf
template:
src: www.conf.j2
dest: /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
backup: yes
#启动
- name: start php
systemd:
name: php-fpm
enabled: yes
state: restarted
php/templates/php.repo.j2
[php]
name=PHP
baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos/$releasever/SCL/$basearch/scl-utils/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
php/templates/www.conf
[www]
listen = 127.0.0.1:9000
listen.allowed_clients = 127.0.0.1
listen.owner = \{\{ web_user \}\}
listen.group = \{\{ web_user \}\}
listen.mode = 0666
user = nginx
group = wordpress
pm = dynamic
pm.max_children = 25
pm.start_servers = 6
pm.min_spare_servers = 2
pm.max_spare_servers = 10
pm.max_requests = 100
pm.status_path = /status
slowlog = /var/log/php-fpm/www-slow.log
catch_workers_output = yes
php_admin_value[error_log] = /var/log/php-fpm/www-error.log
php_admin_flag[log_errors] = on
php_value[session.save_handler] = files
php_value[session.save_path] = /var/lib/php/session
php_value[soap.wsdl_cache_dir] = /var/lib/php/wsdlcache
db
db/tasks/main.yml
#安装MySQL-python
- name: install mysql python
command: yum install -y MySQL-python
#导入MariaDB源密钥
- name: import mariadb source key
rpm_key:
state: present
key: https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB
#创建MariaDB源文件
- name: create mariadb repo
template:
src: mariadb.repo.j2
dest: /etc/yum.repos.d/mariadb.repo
#安装MariaDB
- name: install MariaDB
yum:
name: MariaDB-server
state: present
#启动MariaDB服务
- name: start MariaDB
systemd:
name: mariadb
state: restarted
#创建数据库
- name: create database
mysql_db:
login_user: root
login_password: root
name: blog
state: present
#添加用户
- name: add db user
mysql_user:
login_user: root
login_password: root
name: lidao
password: "lidao"
priv: "*.*:ALL"
state: present
host: "\{\{ item \}\}"
with_items:
- "localhost"
- "192.168.10.%"
db/templates/mariadb.repo.j2
[mariadb]
name = MariaDB
baseurl = https://mirrors.aliyun.com/mariadb/yum/10.4/centos7-amd64/
gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/mariadb/yum/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB
gpgcheck = 1
调试roles
服务部署
top.yml
- hosts: web
gather_facts: false
roles:
- role: basic
- role: nginx-web
- role: php
- hosts: db
roles:
- role: db
发放公钥
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub 192.168.10.133
执行命令
ansible-playbook -i inventory top.yml
总结
- 通过服务部署及配置流程,转换为对应的步骤
- 根据步骤转换为模块
- 书写剧本
- 安装:使用模块
- 配置:使用模块
- 启动与使用:使用模块
- 最后书写剧本(roles)
Ansible jinja2模版
- 应用场景,通过template模块分发
.j2文件,解析文件里面的变量 - 判断,循环功能生产html页面
Ansible优化
-
性能
- ssh服务优化,关闭UseDNS,GSSAPIAuthentication
- yum安装本地安装
- 调整并发数量(-f 调整并发数量,默认是5 ansible.cfg forks=5)
- 给ansible配置缓存,队列
- 分组操作
- 关闭gather_facts,如果不用facts变量可以关闭,剧本中:gather_facts: false配置文件:gathering = explicit
- 关闭hostkey check一般使用密码认证的时候需要关闭
-
安全
-
配置vpm,jumpserver一起使用
-
给变量文件进行加密(ansible-vault)
ansible-vault encrypt/decrypt group_vars/all/main.yml-
ansible-playbook -i hosts top.yml --ask-vault-pass
-
-